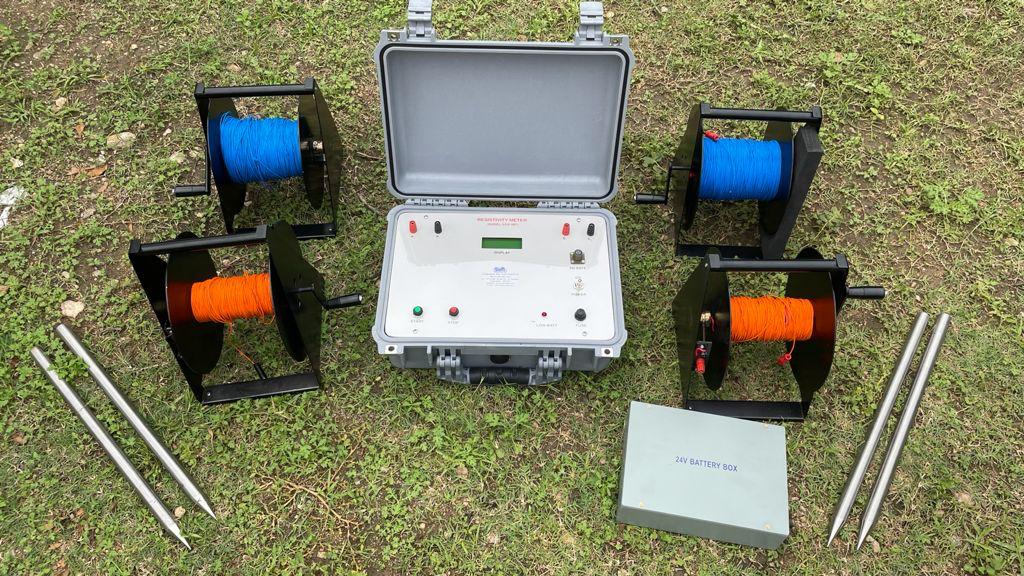
Hydro Geological Survey
A geohydrological survey also referred to as hydrogeological or groundwater survey, is an investigation of the hydrologic and geologic parameters at the subsurface level in a particular area. Hydrogeological maps may be formulated with the data gathered during such a study. It involves the detailed evaluation of the water-bearing levels of rocks and their capability for filtration. Moreover, the intrinsic ability of these rocks to either store or resist water is also assessed. The pressure, type and quality of the underground water is noted, delving into the intensity of the water flow through pores or fractures.
A hydrogeological survey is done to determine the underground water level. Hydrogeological surveying is conducted prior to drilling a borewell in order to ascertain the quality and quantity of water available at a particular location.
Hydrogeological surveys may be conducted on a large, medium or small scale depending upon the purpose of the procedure. Firstly, researched data from government and private agencies that are already available is assessed, followed by extensive field work as needed.


A small-scale survey (1:1,000,000-1:500,000) is done in areas that have never been investigated previously, to gather preliminary information of the hydrogeological condition. These comprise details regarding the ability of the rocks in the area to retain water and overall underground water quality. Medium-scale surveys ((1:200,000-1:100,000) are more elaborate, conducted to collate information for hydrogeological mapping. Water-bearing complexes are mapped and a specific study is conducted regarding the retentive capacity of the rocks in the region.
Large-scale hydrogeological surveys (1:50,000and greater) are mostly initiated in order to deal with precise issues at the stage of engineering and operational planning. Areas, where water collection can be done, are identified and underground water reserves are examined through this type of survey. Medium and large-scale surveys also require drilling procedures, evaluation of the composition of the underground water and its quantity along with a proper measure of its flow. Construction of wells and pumping tests may be performed to understand the hydrogeological condition thoroughly.